Bakre korsbandsskade (PCL): Årsaker, symptomer og behandling
A posterior cruciate ligament injury, also known as a PCL (Posterior Cruciate Ligament) injury, is a less common but serious knee injury that can have significant consequences for the stability and function of the knee. In this article, we will review what a posterior cruciate ligament injury is, its causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
What is a posterior cruciate ligament injury?
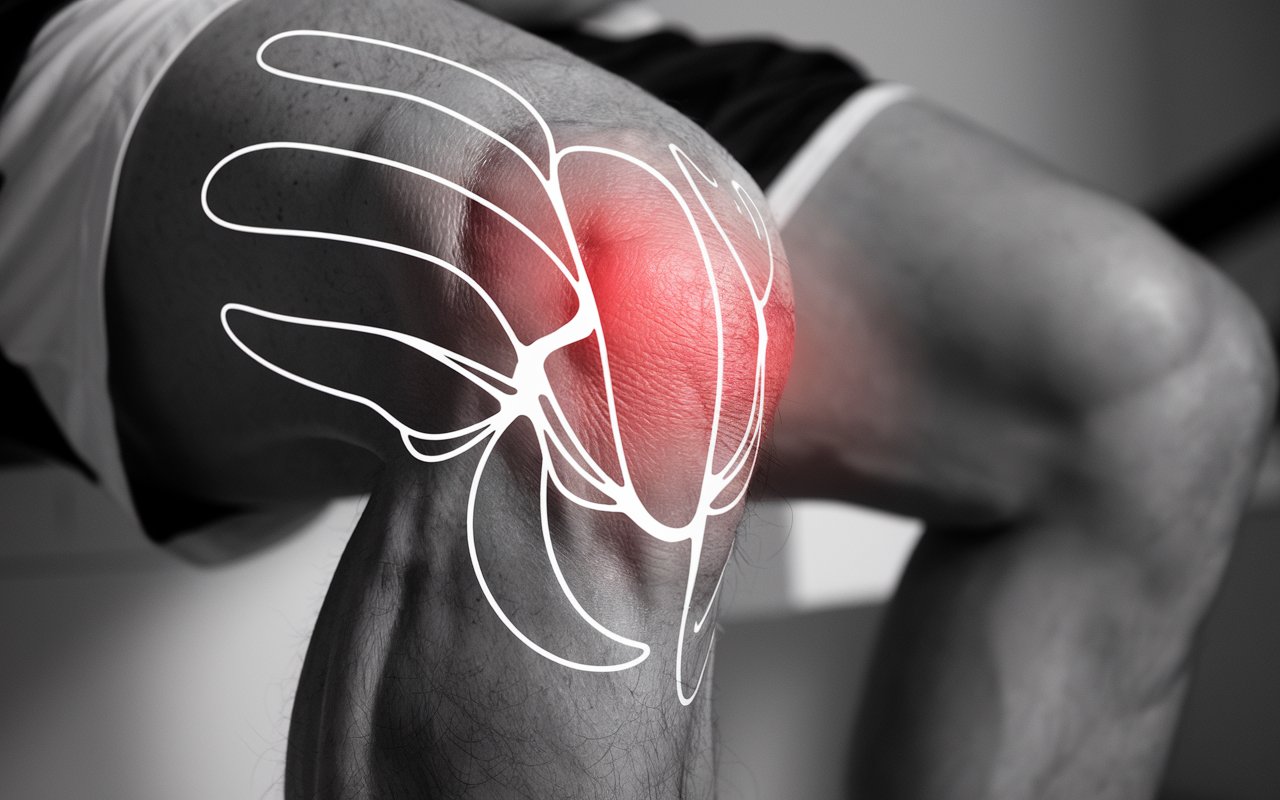
The posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) is one of the four major ligaments in the knee. It sits inside the knee joint and crosses the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL). PCL
Its main function is to prevent the lower leg from sliding backward in relation to the thigh bone (femur). This posterior ligament of the knee is crucial for the stability of the knee. An injury to this ligament can range from a slight stretch to a complete rupture, affecting the function of the knee to varying degrees.
Where is the cruciate ligament located?
The cruciate ligaments, both the anterior (ACL) and posterior (PCL), are located centrally in the knee joint. They cross each other in an X-shape, hence the name "cruciate ligament". Where exactly is the cruciate ligament located? The PCL extends from the back of the shinbone (tibia) to the front of the thighbone (femur). This location means that it plays an important role in stabilizing the knee, especially during bending (flexion) and extension. The posterior cruciate ligament works together with the lateral ligaments to provide stability to the knee joint and prevent abnormal movement of the lower leg. You can also read about anterior cruciate ligament injury here.
Causes of posterior cruciate ligament injury
Posterior cruciate ligament injuries are less common than anterior cruciate ligament injuries and are often caused by:
- Direct force to the front of the knee when it is bent, such as in a car accident (dashboard injury)
- Drop to a bent knee with your toes pointing downwards
- Hyperextension of the knee
- Twisting or hyperextension of the knee during trauma
- Injuries related to sports where the knee is exposed to heavy strain
At the time of injury, the patient can often hear a distinct sound and experience immediate pain. In some cases, the injuries can be combined with damage to other structures in the knee, which complicates diagnosis and treatment. Also read about the dislocated knee .
The symptoms of a posterior cruciate ligament injury can vary in intensity. ACL injury symptoms and ligament injury symptoms often overlap, but there are some specific signs of a torn ACL in the knee. Here is an overview of the most common symptoms:
- Symptom Description
- Pain Often located at the back of the knee, may worsen with flexion
- Swelling Can occur quickly after the injury (hemarthrosis)
- Instability Feeling that the knee is "giving way", especially when walking up stairs
- Difficulty in fully bending the knee
- Tenderness when touching the back of the knee
- Stiffness Especially after extended periods of inactivity
It is important to note that the symptoms of a posterior cruciate ligament injury may be less obvious than those of an anterior cruciate ligament injury, which sometimes leads to delayed diagnosis. If left untreated, the injury can lead to long-term instability and an increased risk of osteoarthritis.
Diagnosis and treatment
If you suspect a posterior cruciate ligament injury, you should seek medical attention immediately. Diagnosis is usually made through a combination of a physical examination, imaging (MRI or X-ray), and specific clinical tests where the doctor examines the stability of the knee.
Treatment for a posterior cruciate ligament injury depends on the severity of the injury and may include:
- Conservative treatment with physiotherapy, rest, and the use of knee braces for less serious injuries
- Surgical reconstruction of the PCL in more serious injuries such as a total rupture or for athletes with high demands on the function of the knee
- Rehabilitation exercises to rebuild strength and stability
- Use of orthotics or knee braces to support the knee during the healing process
Knee pads for cruciate ligament injuries
A specially designed knee brace for cruciate ligament injuries, such as the Knee Pad for ACL Injury from Komforten, can be a valuable aid in rehabilitation and prevention of further injuries. This knee brace offers several benefits:
- Benefit Description
- Increased stability Provides extra support to the knee joint and partially replaces the function of the damaged posterior knee ligament
- Reduced load Relieves the injured cruciate ligament and helps control the movement of the tibia in relation to the femur
- Improved proprioception Increases awareness of the knee's position which reduces the risk of new injuries
- Pain relief Can reduce discomfort during movement by limiting abnormal strain
- Swelling Control Helps reduce and control swelling (hemarthrosis) after injury
The knee brace is designed to provide optimal support without restricting mobility unnecessarily, making it suitable for both rehabilitation and daily activities. For the patient with a damaged cruciate ligament knee, the right orthosis can mean the difference between slow and effective rehabilitation. Read more about pain in the back of the knee .
Buy nowPreventive measures
To reduce the risk of cruciate ligament injuries, including posterior cruciate ligament injuries, it is recommended:
- Regular strength training for legs and torso
- Improving landing technique and movement awareness
- Balance and coordination exercises
- Using the right equipment and knee pads when playing sports
- Special training to strengthen the muscles around the knee
These measures are especially important for people who have previously had a ligament injury or who participate in sports with a high risk of knee injuries.
Conclusion
A posterior cruciate ligament injury is a serious knee injury that requires careful diagnosis and treatment. With proper care, including physical therapy and the use of supportive devices such as knee braces, most patients can return to their normal activities. It is important to follow the rehabilitation plan carefully and be patient during the healing process to achieve the best possible results and reduce the risk of future injuries and the development of osteoarthritis. Read more about osteoarthritis of the knee .
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
How long does it take to recover from a posterior cruciate ligament injury?
Recovery time varies depending on the severity of the injury and the treatment method chosen. With conservative treatment, it can take 4-6 months before you can return to full activity. After surgical reconstruction, rehabilitation can take 9-12 months or longer. More about rehabilitation times for knee injuries .
Can I exercise with a posterior cruciate ligament injury?
Yes, but it is important to adapt your training to the injury and follow the advice of your physiotherapist. Focus initially on regaining mobility and strength. Using a knee brace such as the Knee Guard for ACL Injury can provide extra support and security during training.
How do the symptoms differ between anterior and posterior cruciate ligament injuries?
While both can cause pain and instability, posterior cruciate ligament injuries tend to cause less dramatic symptoms initially. PCL injuries often cause more pain in the back of the knee and can cause a sensation of the knee "giving way" when walking up stairs.