Nerveskade i fot: Symptomer, årsaker og behandling
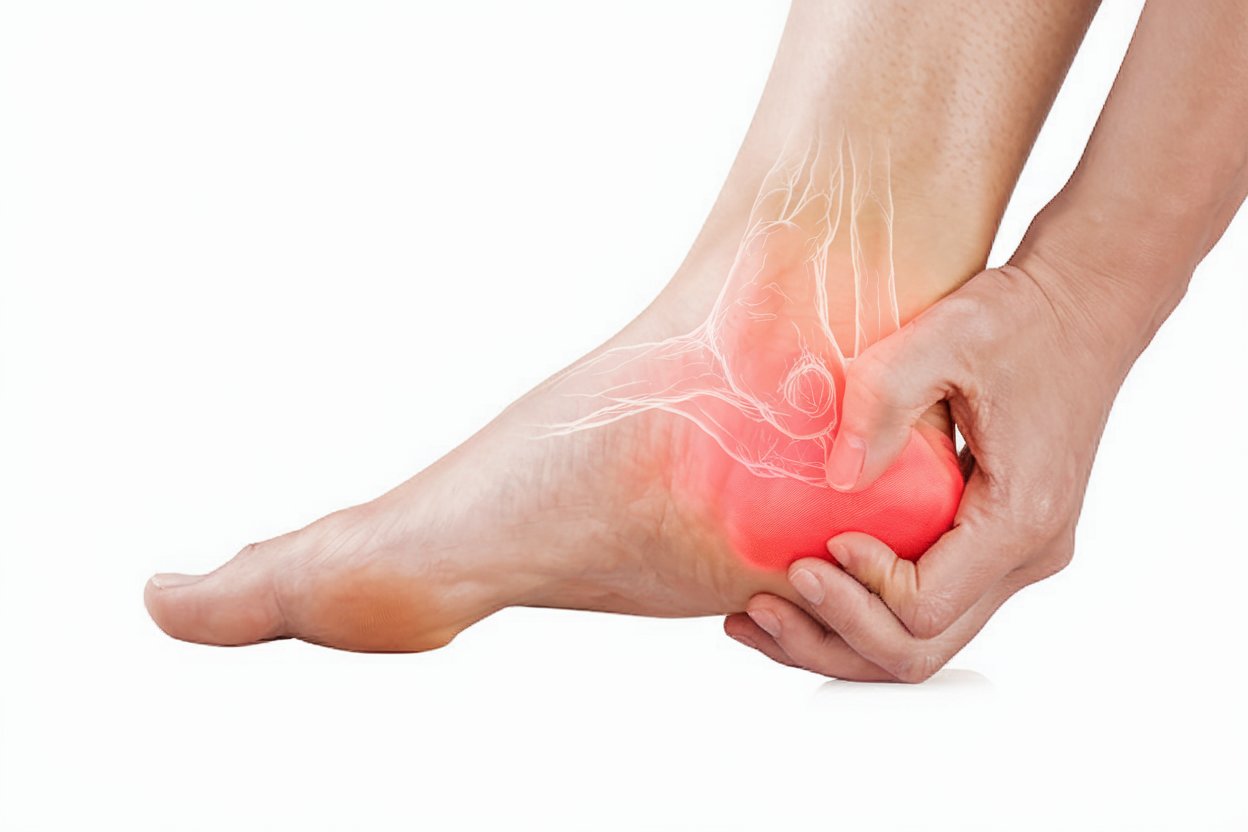
A nerve injury in the foot occurs when one or more nerves in the foot become damaged or irritated. Numbness in the feet can be a significant discomfort and affect mobility. Nerve pain in the foot can be intense and make it difficult to walk or stand for long periods of time. This article reviews the most common symptoms, causes, and treatment options for nerve injury in the foot.
What is nerve damage in the foot?
A nerve injury in the foot occurs when one or more nerves in the foot become damaged or irritated. This can affect peripheral nerves that transmit signals between the foot and the spinal cord, or specific nerves that supply the front of the foot. The damage can affect sensation, motor function, and even the autonomic nervous system, leading to a variety of symptoms such as no sensation in the feet and affecting the function of the foot.
Nerve damage can range from mild conditions that cause temporary discomfort to serious medical conditions such as polyneuropathy, where multiple nerves in the body are affected at the same time. Morton's syndrome is an example of a specific nerve damage that affects the nerve between the toes and causes pain in the forefoot with nerve pain in the foot.
Symptoms of nerve damage in the foot & Numbness in the Feet
Common symptoms include:
- Numbness in the feet and numbness in the foot with tingling in the foot or individual toe
- Burning or stabbing nerve pain in the foot and nerve pain in the foot
- No sensation in the feet or reduced sensation in parts of the foot, especially to touch which can lead to loss of sensation in the toes
- Muscle weakness or paralysis in the foot and calf
- Feeling of walking on pillows with numb feet
- Numbness that can make it difficult to walk
- Changed sensation in the feet
- Pain that worsens at night with nerve pain in the foot
- Balance problems
- Weakness in the muscles of the lower legs
Nerve pain in the foot is often particularly intense and can be described as burning, tingling, or electrical. In patients with diabetes, numbness in the feet can be part of a more extensive polyneuropathy that often begins in the nerves of the legs and can affect both feet symmetrically, such as in polyneuropathy of the feet .
Causes of nerve damage in the foot
Nerve damage in the foot can be caused by several factors that affect the nerves in the foot:
- Trauma or injury to the foot that directly damages the nerve
- Compression of nerves, such as from tight shoes that pinch the nerve fibers
- Diabetes (diabetic neuropathy) - the most common cause of peripheral neuropathy which can cause no feeling in the feet and numbness in the foot
- Surgical procedures in the foot that may lead to unintentional nerve damage
- Systemic diseases such as polyneuropathy, a disease that affects multiple nerves
- Deficiency of certain B vitamins, especially B12, which are important for nerve function in the foot
- Inflammatory conditions affecting the nerve fibers
- Hereditary polyneuropathy affecting the peripheral nervous system
- Autonomic nerves can also be affected in certain types of nerve damage.
The cause of neuropathy can sometimes be difficult to determine. Diabetic feet , which often involve nerve pain and decreased sensation in the feet, is a common consequence of long-term blood sugar damage to the nerve fibers.
Diagnosis and treatment of nerve damage in the foot
Diagnosis and treatment of nerve damage in the foot
Nerve damage in the foot can cause tingling, numbness, weakness, or pain.
The condition often occurs after prolonged pressure on a nerve, injury, diabetes, or circulation problems.
A thorough examination is crucial to determine the extent of the damage and choose the right treatment to support healing and function.
Physical examination
The doctor assesses sensation, reflexes, and muscle strength in the foot to identify any abnormalities.
Advantages of compression stockings: Improves blood circulation and promotes recovery in the affected area.
Nerve conduction test (electroneurography)
This test measures how fast nerve signals travel in the foot and shows where the damage is located.
Advantages of compression stockings: Reduces swelling and discomfort by stimulating blood flow.
MRI
Used to visualize soft tissues, nerves, and any structural damage affecting nerve function.
Advantage: Provides support during the healing process when combined with physical therapy and rest.
EMG (electromyography)
Measures how muscles respond to nerve impulses and can show whether the nerve is partially or completely damaged.
Advantage: Customized shoes or insoles can reduce stress and provide greater comfort when walking.
Sensory examination
Assesses how well different parts of the foot respond to touch and temperature. If abnormalities are found, specialized care may be needed.
Advantage: Compression stockings and supportive aids can improve circulation and promote healing.
Important to consider
If nerve damage in the foot is suspected, seek medical attention for a thorough neurological examination.
Tests such as electroneurography (ENG) and electromyography (EMG) help determine nerve function and the extent of the damage.
Early treatment—such as physical therapy, custom shoes, and compression stockings—can make a big difference in recovery.
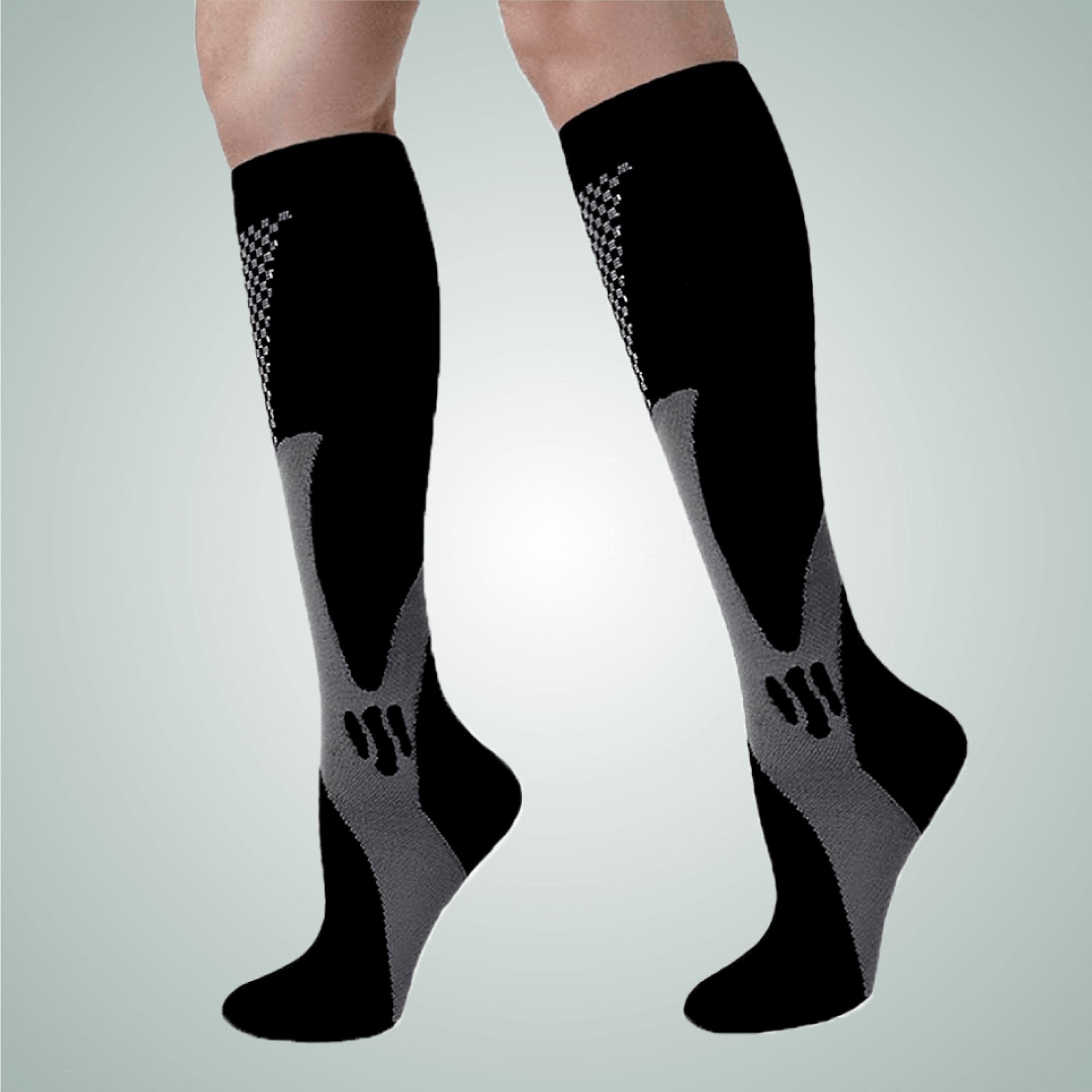

How compression stockings can help with nerve damage in the foot
Compression stockings from Komforten can be an effective aid for nerve damage in the foot by:
- Improve blood circulation in the foot and leg
- Reduce swelling and discomfort that can worsen nerve pain in the foot
- Provide support during daily activities and exercise
- Potentially relieve some symptoms such as tingling and burning sensation
- Provide even compression that can reduce pressure on nerves in the foot
- Be part of different types of aids to manage the discomfort
Especially for people with circulation-related nerve problems, such as burning feet , compression stockings can be a valuable part of the daily management of nerve pain in the foot and numbness in the feet.
Buy nowConclusion
Nerve damage in the foot can be painful and limiting, but with proper diagnosis and treatment, many patients can experience significant improvements in foot numbness and nerve pain in the foot. Using compression stockings can be part of an overall treatment plan to improve comfort and support the healing process. It is important to consult a doctor for a proper diagnosis and individualized treatment plan, especially if the nerve damage occurred after surgery.
For more complex nerve injuries, the patient may need to be referred to specialized care for extensive treatment. Treatment should always be tailored to the specific type of nerve injury and the patient's individual circumstances. A possible consequence of nerve injury is also foot drop , where paralysis of the foot muscles affects walking function.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Can nerve damage in the foot heal on its own?
Some mild nerve injuries may heal over time, but more serious injuries often require medical treatment. Nerve fibers have some ability to regenerate, but the process is slow and usually requires supportive treatment.
How long can it take for a nerve injury in the foot to heal after surgery?
Healing time varies depending on the extent of the injury, but can take anywhere from a few weeks to several months. In some cases, full recovery can take up to a year or longer, especially if major nerves are injured.
Can compression stockings help with all types of nerve damage in the foot?
Compression stockings can be helpful for many types of nerve injuries, but are particularly effective for problems related to poor circulation. However, they are not as effective for pure compression injuries or for certain types of hereditary polyneuropathy where circulation is not the problem.
When should I seek medical attention for a suspected nerve injury in the foot?
Seek medical attention if you experience persistent numbness, pain, or weakness in your foot, especially if symptoms do not improve over time. Immediate medical attention should be sought if symptoms develop suddenly or after an injury, or if they are associated with severe pain or disability.
Can I use compression stockings if I have recently had foot surgery?
Always consult your doctor before using compression stockings after surgery, as they may affect the healing process. In some cases, they may be contraindicated initially after surgery, while in other cases they may be recommended as part of rehabilitation.

