Foot Pain: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Treatments

Foot pain can affect your everyday life in many ways. Whether it's a dull ache or a sharp pain, it can limit your ability to walk, stand, and perform daily activities. In this guide, we explore the most common causes of foot pain and different treatment options to help you identify and best treat your foot pain.
Symptoms of Foot Pain
Foot pain can manifest itself in many different ways, and recognizing the symptoms is crucial to identifying the underlying cause. Common symptoms include:
- Aching pain : A constant, dull pain that can be felt throughout the foot or in specific areas.
- Sharp pain : Sudden and intense pain that often occurs with injury or overexertion.
- Swelling : The foot may become swollen, which could be a sign of inflammation or injury.
- Redness and warmth : Areas on the foot may become red and warm, often indicating an infection or inflammation.
- Stiffness : Difficulty moving the foot normally, which may be due to joint problems such as osteoarthritis in the foot.
- Numbness and tingling : The feeling that the foot is "asleep" may indicate nerve compression.
- Burning sensation : A burning pain, especially on the outside of the heel or under the foot, can be a sign of nerve problems.
Common types of foot pain and their causes
Below you will find an overview of common types of foot pain, where they are felt, what causes them, and what key symptoms are typical.
| Typ av smärta | Område | Vanliga orsaker | Nyckelsymtom |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ont på ovansidan | Ovansidan av foten | Överansträngning, stressfrakturer, seninflammation | Smärta vid rörelse, svullnad, ömhet |
| Ont under foten | Undersidan av foten | Plantarfasciit, stressfrakturer, nervinklämning | Skarp smärta vid första steg, ömhet, svullnad |
| Ont i hålfoten | Fotvalvet | Felaktiga skor, överansträngning, plantarfasciit | Smärta vid belastning, ömhet |
| Brännande fötter | Hela foten | Nervproblem, diabetes, långvarig belastning | Brännande känsla, stickningar, domningar |
| Inflammation i foten | Hela foten | Skador, artrit, överansträngning | Svullnad, rodnad, värme, smärta |
| Mortons syndrom | Mellan tårna | Nervinklämning mellan tårbenen | Skarp, brännande smärta, domningar |
| Skräddarknuta | Utsidan vid lilltån | Felaktiga skor, fotdeformiteter | Smärta, svullnad, rodnad |
| Artros i foten | Leder i foten | Ålder, tidigare skador, övervikt | Stelhet, smärta, svullnad |
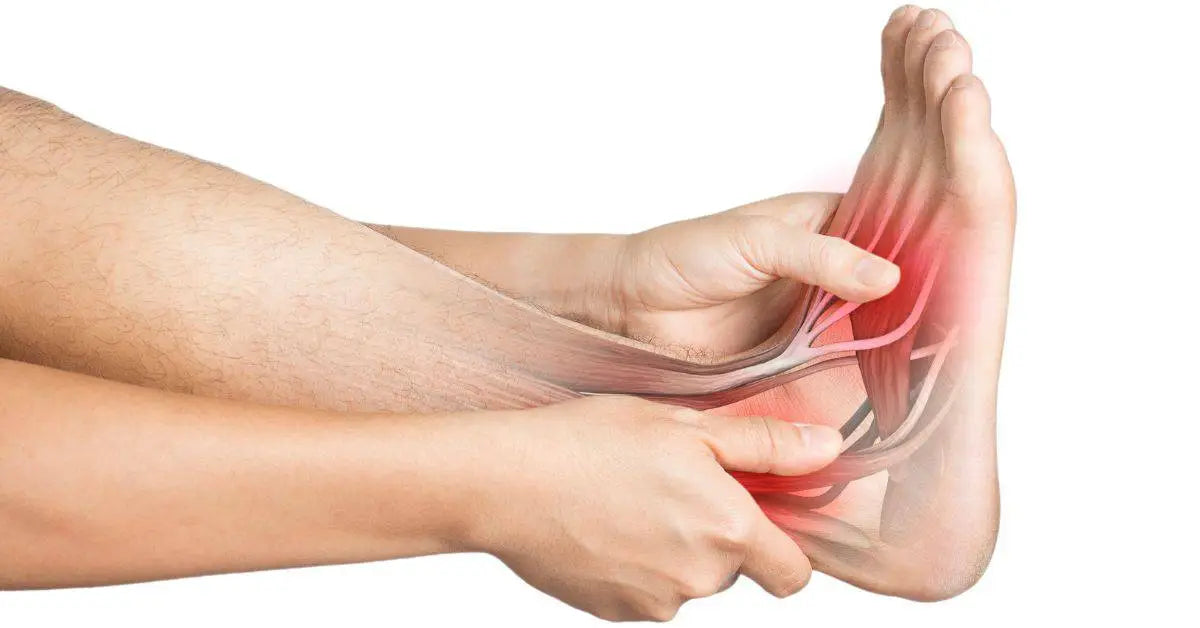
Pain on the top of the foot can have several causes. A common cause is extensor tendinitis, which is inflammation of the tendons that extend the toes. This condition often occurs due to overuse or wearing the wrong shoes. Other causes can include stress fractures, where small cracks form in the bone due to overuse, or inflammation of the ankle joint. Muscles that can be affected by extensor tendinitis include the extensor digitorum longus and the extensor hallucis longus.
Extensor Tendonitis Treatment
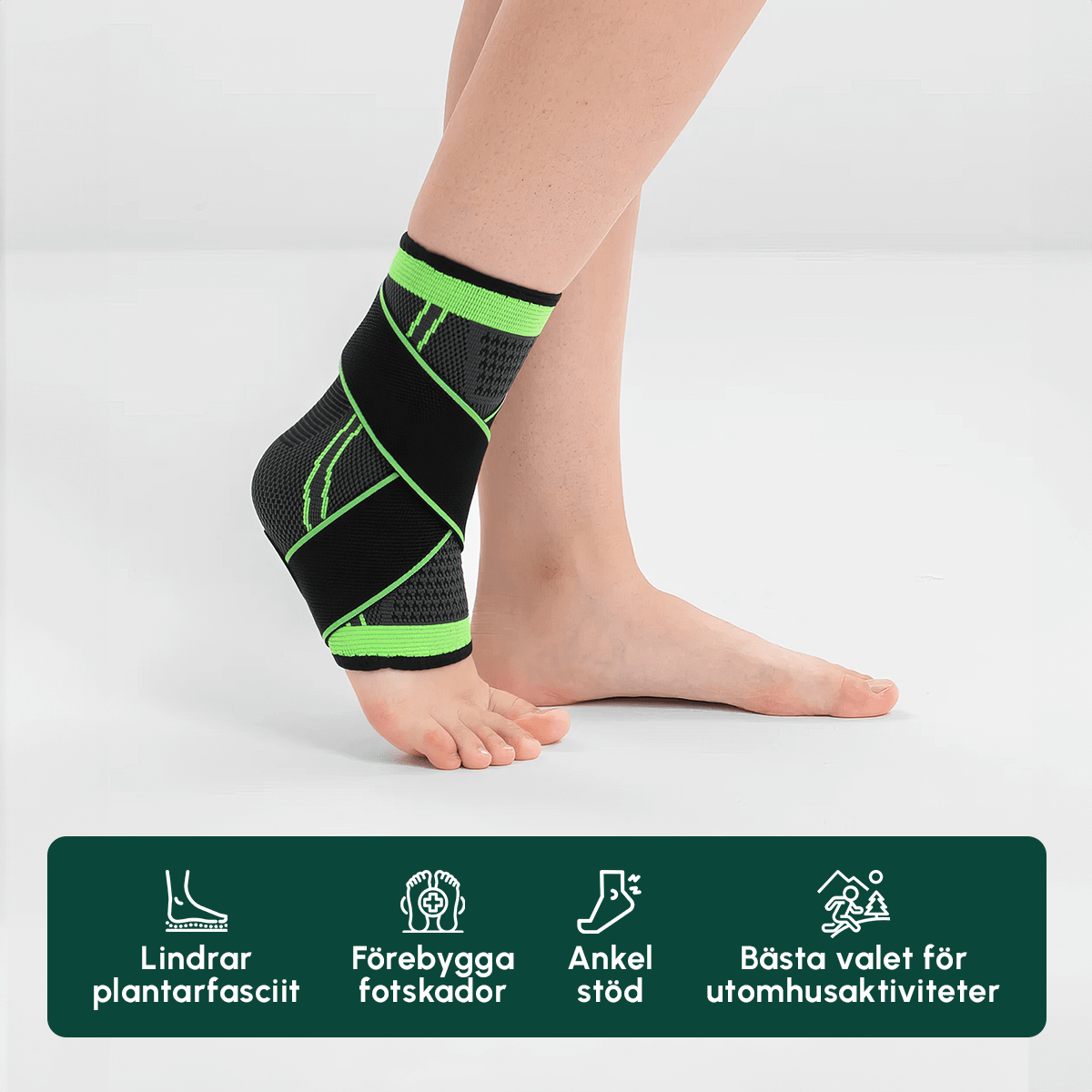
If you have extensor tendonitis, our specially developed Foot Support™ is an effective first step. It provides stability to your feet, reduces strain on the tendons, and relieves pain with every step. The Foot Support™ is especially good for those who have pain on the top or bottom of the foot, as well as osteoarthritis in the foot.
In addition to using The Foot Support™, the following treatment methods can help you recover:
- Rest and ice: Resting the foot and applying ice to the affected area reduces inflammation and relieves pain.
- Compression and elevation (RICE method): Using compression and elevating the foot can help reduce swelling faster.
- Supportive shoes or inserts: Shoes that provide good support, or inserts that relieve the pressure on the foot, can reduce the strain on the tendons.
- Medical treatment or physiotherapy: In more severe cases, physiotherapy can help strengthen muscles and restore mobility, while anti-inflammatory drugs reduce pain and swelling.
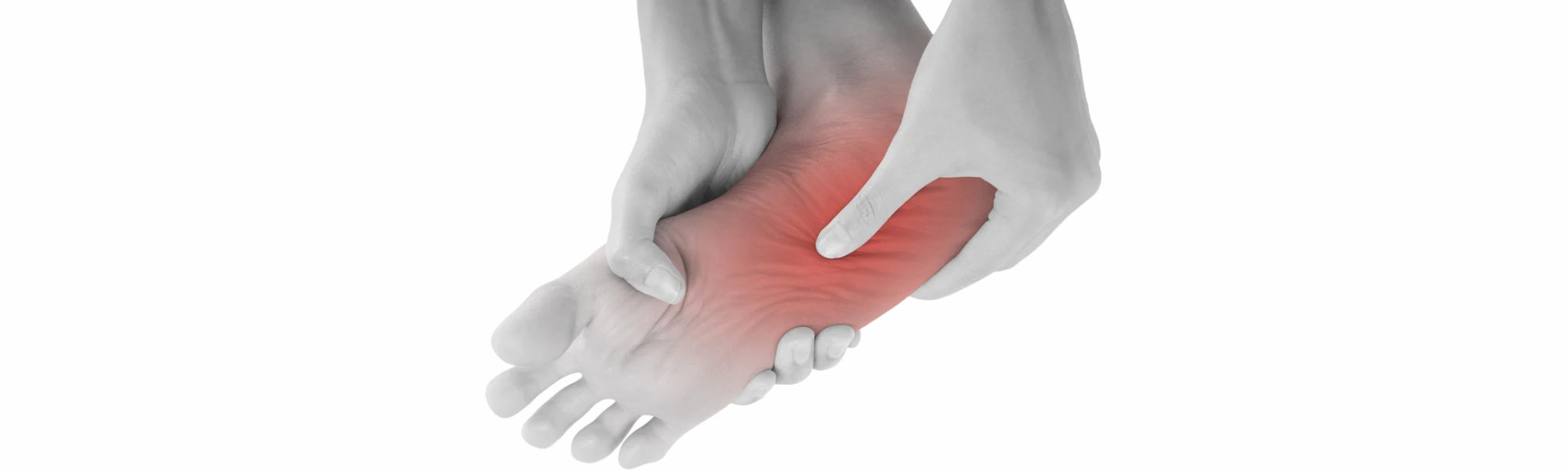
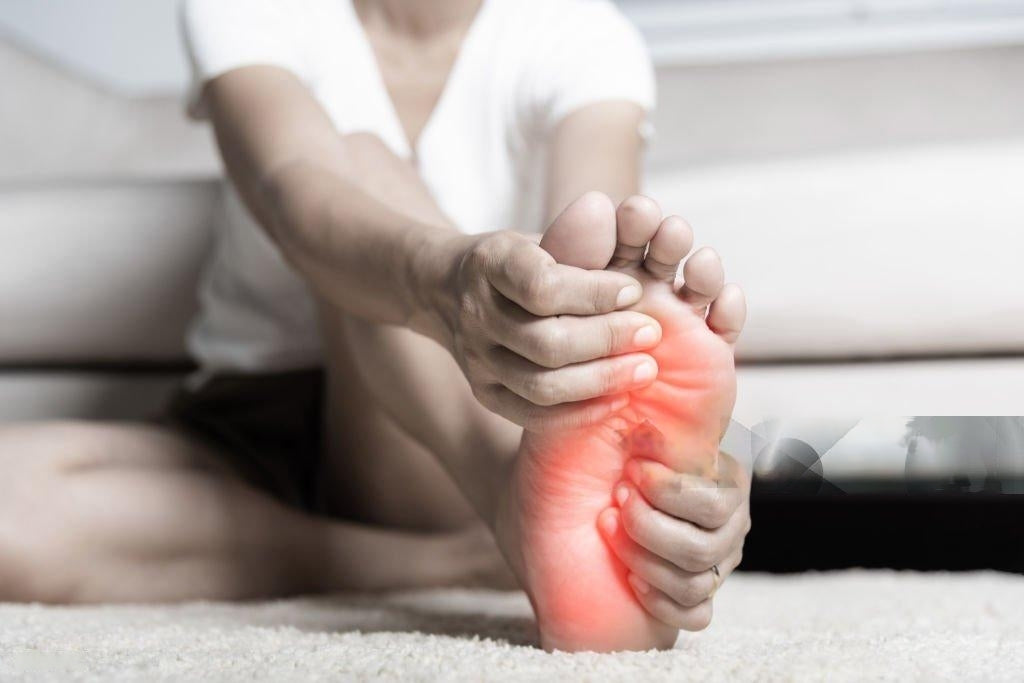
Pain in the bottom of the foot is often related to conditions such as plantar fasciitis, which is an inflammation of the thick connective tissue that runs along the bottom of the foot. This can be caused by overuse, improper footwear, or prolonged standing. Other possible causes include stress fractures and nerve compression. Muscles that may be affected include the flexor digitorum brevis and abductor hallucis.
Treatments may include:
- Stretching
- Orthopedic inserts
- Anti-inflammatory drugs
- Physiotherapy
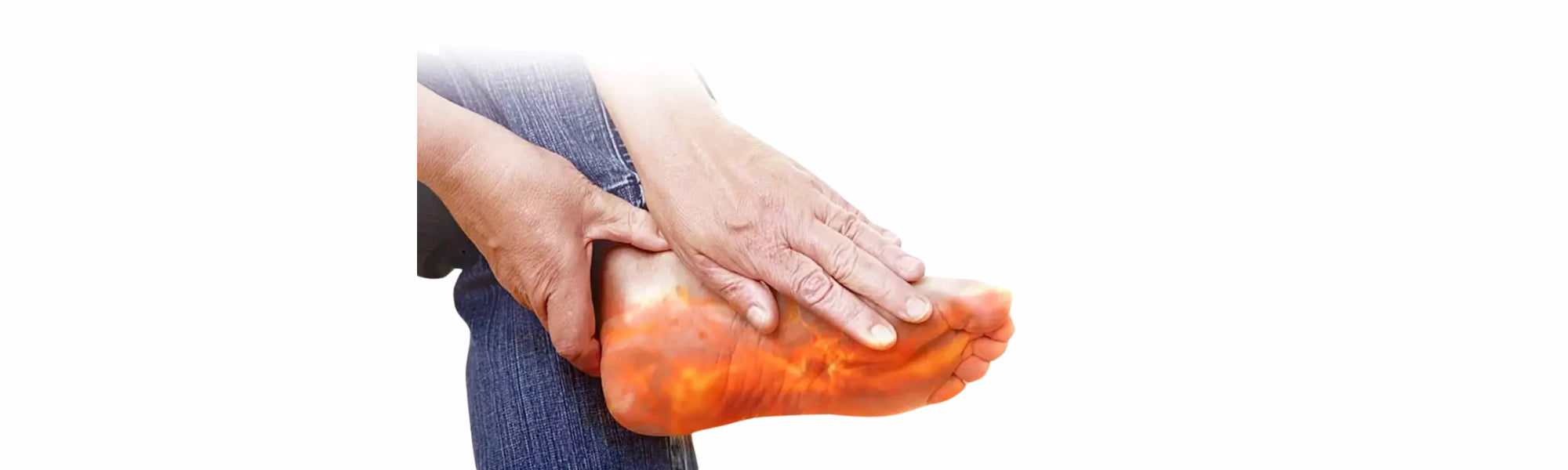
Burning feet can be a result of nerve problems, such as neuropathy, where the nerves in the feet become damaged or inflamed. This can be caused by diabetes, alcohol abuse, or vitamin deficiencies. Symptoms include a burning sensation, tingling, and sometimes numbness. Muscles that can be affected include the small muscles in the foot such as the interossei and lumbricals.
Treatments may include:
- Avoiding triggers
- Cooling creams
- Medical treatment for underlying conditions
- EMS massager
Inflammation in the foot can be caused by injury, overuse, or conditions such as arthritis. Common symptoms include swelling, redness, warmth, and pain. The inflammation can affect various structures in the foot, including tendons, muscles, and joints. Muscles that can be affected include the flexor digitorum longus and tibialis posterior.
Treatments may include:
- Rest and Ice
- Anti-inflammatory drugs
- Physiotherapy or medical treatment
- Compression stockings
Morton's disease is a pinched nerve between the toes, most often between the third and fourth toes. This can be caused by narrow shoes, overuse, or a sunken arch. Symptoms include sharp pain, burning, and numbness in the forefoot. The nerve most often affected is the common plantar digital nerve.
Treatments may include:
- Stretching
- Orthopedic inserts
- Anti-inflammatory drugs
- Physiotherapy
- Shock-absorbing soles
- OrthoShoes that relieve nerve compression and improve foot comfort
A bunion is a bulge on the outside of the foot at the little toe, often caused by ill-fitting shoes or foot deformities. This condition can lead to pain, swelling, and redness. The malposition causes the little toe to turn inward toward the adjacent toe, making the joint of the little toe more prominent and sensitive to pressure. Muscles that may be affected include the abductor digiti minimi.
Treatments may include:
- Wider shoes
- Protective pads
- Anti-inflammatory drugs
- Surgery
Osteoarthritis of the feet is a degenerative joint disease that causes pain, stiffness, and swelling. Common causes include age, obesity, and previous injuries. Osteoarthritis can affect several joints in the foot, including the metatarsal joints and the joints of the toes. Muscles that can be affected include the small muscles of the foot such as the interossei and lumbricals, as well as larger muscles such as the tibialis anterior and posterior.
Treatments may include:
- Anti-inflammatory drugs
- Physiotherapy
- Supportive shoes or inserts
- Surgery
Foot pain can have many different causes, and understanding these can help you identify the right treatment and prevent future problems. Here are some common causes of foot pain:
- Overexertion: Prolonged standing or walking can lead to pain and fatigue in the foot.
- Injuries: Sprains, fractures, or other acute injuries can cause immediate pain.
- Incorrect shoes: Shoes that do not provide enough support or are too tight can lead to pain and deformities.
- Plantar fasciitis: Inflammation of the connective tissue under the foot, often caused by overuse.
- Osteoarthritis of the foot: Wear and tear on the joints that can lead to chronic pain and stiffness.
- Stress fractures: Small cracks in the bone due to overload.
- Diabetes: Can lead to nerve damage and circulation problems that affect the feet.
- Arthritis: Inflammation of the joints that can cause pain and swelling.
- Incorrect walking style: An unnatural walking style can put undue stress on the foot and lead to pain.
- Hallux valgus: A deformity in which the big toe points toward the other toes, which can cause pain and swelling.
- Morton's disease: A pinched nerve between the toes, often between the third and fourth toes, which can cause sharp pain and a burning sensation.
Foot pain prevention
Preventing foot pain is crucial to maintaining good foot health and avoiding future discomfort. By taking proactive steps, you can reduce the risk of injury and overuse, helping you stay active and pain-free.
Effective tactics for preventing foot pain
Wear the right shoes
- Choose shoes that provide good support and fit your foot shape. Avoid tight or high heels that can cause foot pain.
- Replace worn shoes regularly to ensure they still provide adequate support.
Stretch and strengthen your feet
- Perform daily stretching exercises to keep your muscles and tendons flexible. Focus on your arch and Achilles tendon.
- Strengthen your foot muscles by walking barefoot on different surfaces and doing toe raises.
Use orthopedic insoles
- If you have flat feet or high arches, orthopedic insoles can provide extra support and reduce strain on your feet.
- Consult a foot specialist to get custom inserts to suit your needs.
Maintain a healthy weight
- Being overweight can increase the strain on your feet and lead to osteoarthritis in the foot and other problems.
- Strive for a balanced diet and regular exercise to keep your weight under control.
Avoid overexertion
- Vary your activities to avoid putting too much strain on the same parts of your foot.
- Take regular breaks and rest your feet if you stand or walk a lot during the day.
Keep your feet dry and clean
- Wash your feet daily and dry them thoroughly to avoid fungal infections and other skin problems.
- Wear breathable socks and shoes to keep your feet dry.
Listen to your body
- If you feel pain or discomfort in your feet, don't ignore it. Rest and treat the pain early to avoid it getting worse.
- Seek professional help if the pain persists or worsens.
| Behandlingsmetod | Fördelar | Nackdelar |
|---|---|---|
| Vila och is | Enkel och kostnadseffektiv | Kan kräva lång återhämtningstid |
| Stretching och övningar | minskar inflammation och smärta snabbt | inte alltid tillräckligt för allvarliga skador |
| Ortopediska inlägg | Förbättrar flexibilitet och styrka | Kräver regelbundenhet och tid |
| Antiinflammatoriska läkemedel | kan förebygga framtida skador | kan vara smärtsamt i början |
| Fysioterapi | Ger extra stöd och avlastning | Kräver anpassningstid |
| Kirurgi | kan anpassas efter individuella behov | Kan ha biverkningar vid långvarig användning |
| Kompressionsstrumpor | Snabb lindring av smärta och inflammation | behandlar inte grundorsaken |
| Kylande och värmande krämer | lättillgängliga | Kan vara kostsamt och tidskrävande |